BC Provider Location Registry FHIR Implementation Guide
1.0.0 - fhirVersion-4.0; BCPLRVersion=1
BC Provider Location Registry FHIR Implementation Guide
1.0.0 - fhirVersion-4.0; BCPLRVersion=1
BC Provider Location Registry FHIR Implementation Guide - Local Development build (v1.0.0) built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) Build Tools. See the Directory of published versions
| Official URL: http://hlth.gov.bc.ca/fhir/provider/ImplementationGuide/fhir.ca-bc.provider | Version: 1.0.0 | |||
| Active as of 2024-04-28 | Computable Name: BCProviderRegistry | |||
This specification is currently published as a Draft Standard on the ministry github and is not intended for implementation. Feedback is welcome but readers should understand that there is more work to be done in testing the profiles and operations defined in this guide. For more information, please see the Future Plans page in this guide.
The Provider and Location Registry (PLR) is a centralized repository of core information about health service providers, e.g., physicians, nurses, pharmacists. Information is supplied by authorized sources such as professional colleges. PLR ensures the security of provider information by employing or enabling proven security and privacy techniques. Data in the repository is available to authorized organizations to facilitate the transmission of provider information between authorized organizations in real time. This makes PLR a cornerstone in the development of the Electronic Health Record (EHR).
PLR supports BC Health stakeholder needs for a comprehensive, trusted and reliable custodian and source of core health provider, location and facility information. PLR is the authoritative registry of British Columbia healthcare Providers’ demographic and professional information which supports activities such as:
The PLR contains information for each Provider (e.g. personal demographics, College Identifier, Ministry Practitioner Identifier (MPID), license status, expertise, business contact, and work location) which is sourced from professional colleges and regulatory bodies such as the:
Any given point of service (PoS) can only access the Provider data fields that are included in the relevant information sharing agreements with the Ministry of Health. Specific data permissions are set within the PLR. A PoS application can use the PLR as the sole source of Provider information or to complement existing retained Provider information.
A Provider is a person / individual or an organization acting in a role. The PLR uses the terms Individual Provider and Organizational Provider to distinguish between the two types. Examples:
The information recorded for Providers consists of unique identifiers, names, addresses, telecommunication numbers, electronic addresses, expertise, credentials, statuses, conditions, notes, relationships, disciplinary actions, and work locations. Information for Individual Providers also includes demographic details.
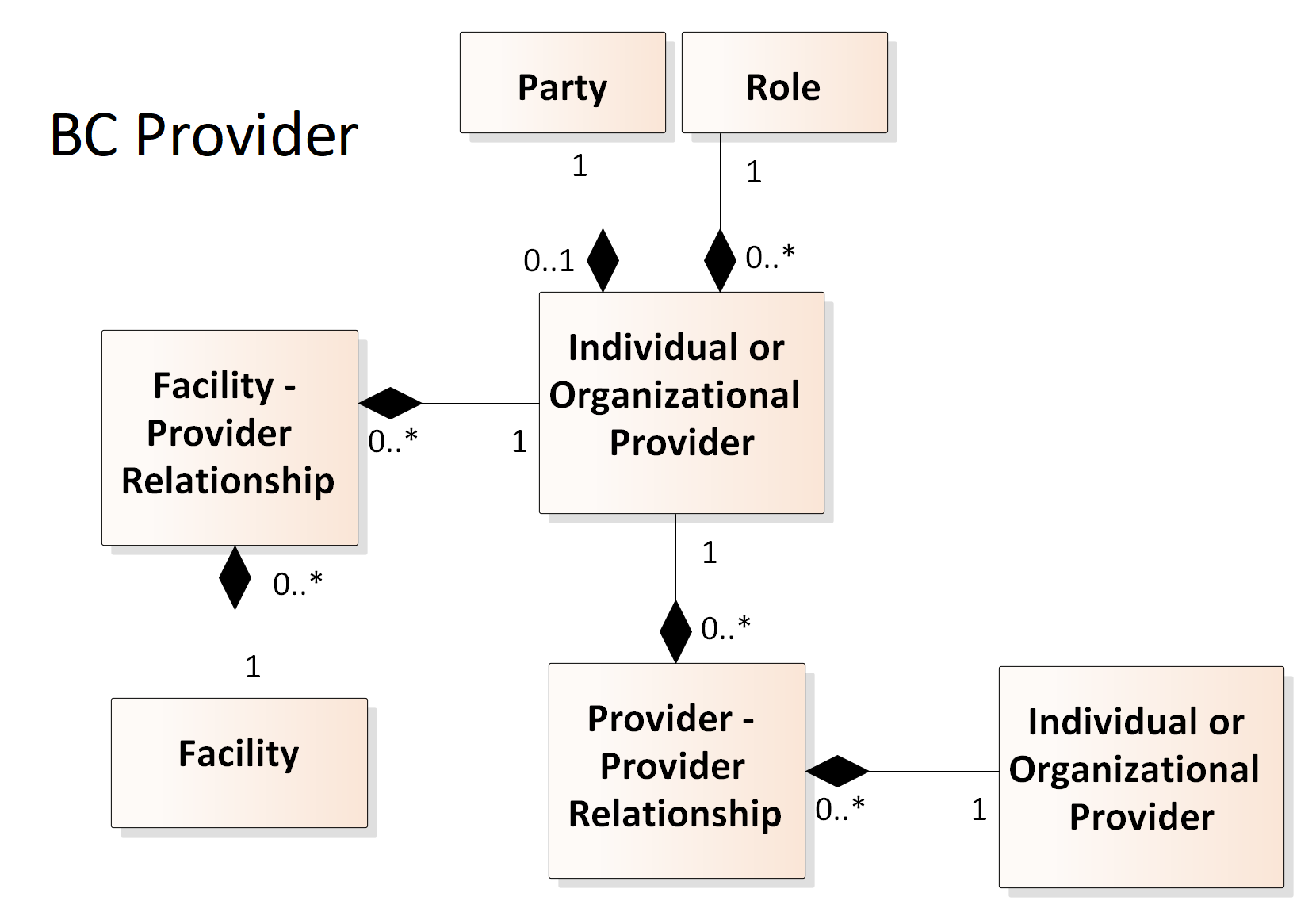
The relationships above are compositions, the children cannot exist without the parent(s). I.e. the Individual or Organization Provider cannot exist without a Party and Role. And each of the Facility-to-Provider or Provider-to-Provider relationships must be connected to existing Facilities or Providers.
A Facility is an identified, named place, piece of equipment, or amenity of interest to BC Health which is physical (e.g. a building or vehicle). It can be a a particular place or position which may be physically/spatially related. Facilities have names, and may have other communication mechanisms: mailing addresses, telephone numbers, etc. As well, multiple organizations can be related to a facility.
A Facility is a unique civic address in BC and may be:
Examples: Long term care facility, Walk-in Clinic, Urgent Care Centre, Public Health Office, Hospitals, Ambulances, Pharmacies, Laboratory offices, Community Medical Imaging Clinics.
The PLR concept of a Providers Work Location will be promoted to an independent entity called Facility. Facilities are stand-alone objects that may be related to, and only to, providers through relationships.
This enables:
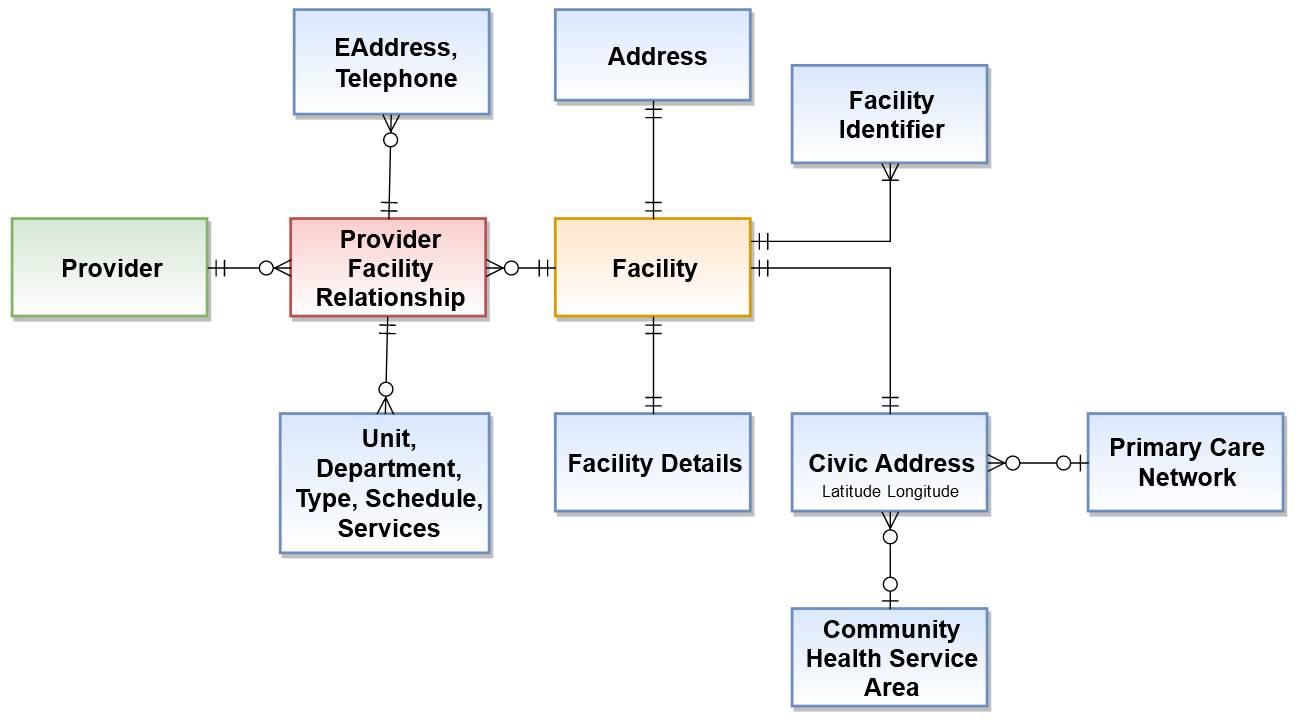
The above diagram outlines the different entities that compose a facility:
This Implementation Guide was written based on resource profiles from CA Baseline where available (Practitioner, Organization, and Location) and otherwise from FHIR R4 (OrganizationAffiliation and PractitionerRole). At this time this IG is conformant with the CA Baseline.
The PLR User Guide provides a detailed overview of the current PLR functionality. Please contact the registry administrator to request a copy of the User Guide.
Conformance verbs - SHALL, SHOULD, MAY - used in this guide are defined in FHIR Conformance Rules.
No form of data absent reason is supported; mandatory data must always be present.
All of the PLR Profiles include elements that are marked as ‘Must Support’. For the purposes of this guide, Must Support is intended to represent those fields that will be exchanged between client applications and the PLR server. Client applications who are receving PLR information SHALL be able to receive all fields marked as Must Support without raising an exception. When sending information to the PLR server, client applications SHOULD be able to send any fields marked as Must Support.
The privacy and security requried to handle PLR data is fully described in the conformance guides.