Easily generate bar plots using ggplot2 with a simplified
customization interface for common modifications with static (ggplot) and
interactive (plotly) output options. The static output is useful for
producing static reports (e.g. for manuscripts) and is readily customized
further using ggplot2 syntax. The interactive output is helpful for
exploring the data and producing dynamic html reports. To plot a bar graph
of sample means or medians and error bars, see
plot_stat_error instead. See
this
blog post for an introduction to ggplot2.
plot_bar(
data,
x = NULL,
y = NULL,
...,
width = 0.85,
position = c("dodge", "fill", "stack"),
dodge_padding = 0.1,
fill_var = NULL,
colour_var = NULL,
xlab = NULL,
ylab = NULL,
title = NULL,
title_hjust = 0.5,
caption = NULL,
caption_hjust = 0,
fill_var_title = NULL,
colour_var_title = NULL,
ylim = c(NA, NA),
ybreaks = ggplot2::waiver(),
transform_y = FALSE,
y_transformation = "log10",
y_var_labs = ggplot2::waiver(),
x_var_order_by_y = NULL,
x_var_order = NULL,
fill_var_order_by_y = NULL,
fill_var_order = NULL,
colour_var_order_by_y = NULL,
colour_var_order = NULL,
x_var_labs = NULL,
fill_var_labs = NULL,
colour_var_labs = NULL,
fill_var_values = NULL,
colour_var_values = NULL,
palette = c("plasma", "C", "magma", "A", "inferno", "B", "viridis", "D", "cividis",
"E"),
palette_direction = c("d2l", "l2d"),
palette_begin = 0,
palette_end = 0.9,
alpha = 0.8,
greyscale = FALSE,
line_size = 1,
coord_flip = FALSE,
theme = c("bw", "classic", "grey", "light", "dark", "minimal"),
text_size = 14,
font = c("sans", "serif", "mono"),
facet_var = NULL,
facet_var_order = NULL,
facet_var_labs = NULL,
facet_var_strip_position = c("top", "bottom"),
facet_var_text_bold = TRUE,
legend_position = c("right", "left", "top", "bottom"),
omit_legend = FALSE,
interactive = FALSE,
aesthetic_options = FALSE
)Arguments
- data
A data frame or tibble containing at least one categorical variable.
- x
A categorical variable you want to obtain separate bar plots for (quoted or unquoted), e.g. x = "variable" or x = variable. If you want to plot all bars on top of each other (position = "fill" or position = "stack") to form a single banded bar leave "x" blank and assign a variable to either fill_var or colour_var instead. N.B. failing to assign a variable to x will also remove x-axis ticks and labels.
- y
A numeric variable containing the values you would like plotted on the y-axis (quoted or unquoted), e.g. y = "variable" or y = variable. If y is not specified, then the stat = "count" option will be used for
geom_barand the counts of the variable(s) assigned to x, fill_var, and/or colour_var will be plotted on the y-axis.- ...
graphical parameters (not associated with variables) to be passed to
geom_bar, e.g. colour or fill, to be applied to all bars. To see some of the available options in a web browser, set the aesthetic_options argument to TRUE.- width
Adjusts the width of the bars (default = 0.85).
- position
Determines how bars are arranged relative to one another when a grouping variable is assigned to either fill_var or colour_var. The default, "dodge", uses
position_dodge2to arrange bars side-by-side; "stack" places the bars on top of each other; "fill" also stacks bars but additionally converts y-axis from counts to proportions (assuming y argument is unspecified).- dodge_padding
If position = "dodge", this controls the gap width between adjacent bars (default = 0.1). To eliminate the gap, set this to 0. To overlay bars use a negative value e.g. -0.5. See
position_dodge2for details.- fill_var
Use if you want to assign a variable to the bar fill colour, e.g. fill_var = "grouping_variable" or fill_var = grouping_variable. Produces separate sets of bars for each level of the fill variable. See
aesfor details.- colour_var
Use if you want to assign a variable to the bar outline colour, e.g. colour_var = "grouping_variable" or colour_var = grouping_variable. Produces separate sets of bars for each level of the colour variable. See
aesfor details.- xlab
Specify/overwrite the x-axis label using a character string, e.g. "x-axis label"
- ylab
Specify/overwrite the y-axis label using a character string, e.g. "y-axis label"
- title
Add a main title to the plot using a character string, e.g. "bar plots of y for each group of x"
- title_hjust
Left-to-right/horizontal justification (alignment) of the main plot title. Accepts values from 0 (far left) to 1 (far right). Default is 0.5 (centre).
- caption
Add a figure caption to the bottom of the plot using a character string.
- caption_hjust
Left-to-right/horizontal justification (alignment) of the caption. Accepts values from 0 (far left) to 1 (far right). Default is 0 (left).
- fill_var_title
If a variable has been assigned to fill using fill_var, this allows you to modify the variable label in the plot legend.
- colour_var_title
If a variable has been assigned to colour using colour_var, this allows you to modify the variable label in the plot legend.
- ylim
specify the y-axis limits, e.g. ylim = c(lower_limit, upper_limit). Use NA for the existing minimum or maximum value of y, e.g. the default is ylim = c(NA, NA)
- ybreaks
This allows you to change the break points to use for tick marks on the y-axis.
seqis particularly useful here. Seescale_y_continuousfor details. If ybreaks is specified, then ylim should be also.- transform_y
Would you like to transform the y axis? (TRUE or FALSE)
- y_transformation
If transform_y = TRUE, this determines the transformation to be applied. Common choices include "log10" (the default), "log2", "sqrt", or "exp". See
scale_continuousfor details.- y_var_labs
Allows you to modify the labels displayed with the y-axis tick marks. See
scale_continuousfor details.- x_var_order_by_y
If a variable has been assigned to x, this allows you to sort the bars in order of increasing/ascending ("i" or "a") or decreasing ("d") value of y. If no variable is assigned to y, then the sorting occurs based on relative counts (position = "dodge" or position = "stack") or proportions (position = "fill").
- x_var_order
If a variable has been assigned to x, this allows you to manually modify the order of the variable groups, e.g. x = grouping_variable, x_var_order = c("group_2", "group_1"). See
fct_relevelfor details.- fill_var_order_by_y
If a variable has been assigned to fill_var, this allows you to sort the bars in order of increasing/ascending ("i" or "a") or decreasing ("d") value of y. If no variable is assigned to y, then the sorting occurs based on relative counts (position = "dodge" or position = "stack") or proportions (position = "fill").
- fill_var_order
If a variable has been assigned to fill using fill_var, this allows you to modify the order of the variable groups, e.g. fill_var = grouping_variable, fill_var_order = c("group_2", "group_1"). See
fct_relevelfor details.- colour_var_order_by_y
If a variable has been assigned to colour_var, this allows you to sort the bars in order of increasing/ascending ("i" or "a") or decreasing ("d") value of y. If no variable is assigned to y, then the sorting occurs based on relative counts (position = "dodge" or position = "stack") or proportions (position = "fill").
- colour_var_order
If a variable has been assigned to colour using colour_var, this allows you to modify the order of the variable groups, e.g. colour_var = grouping_variable, fill_var_order = c("group_2", "group_1"). See
fct_relevelfor details.- x_var_labs
If a variable has been assigned to x, this allows you to modify the labels of the variable groups, e.g. x = grouping_variable, x_var_labs = c("group_1_new_label" = "group_1_old_label", "group_2_new_label" = "group_2_old_label"). See
fct_recodefor details.- fill_var_labs
If a variable has been assigned to fill using fill_var, this allows you to modify the labels of the variable groups, e.g. fill_var = grouping_variable, fill_var_labs = c("group_1_new_label" = "group_1_old_label", "group_2_new_label" = "group_2_old_label"). See
fct_recodefor details.- colour_var_labs
If a variable has been assigned to colour using colour_var, this allows you to modify the labels of the variable groups, e.g. colour_var = grouping_variable, colour_var_labs = c("group_1_new_label" = "group_1_old_label", "group_2_new_label" = "group_2_old_label"). See
fct_recodefor details.- fill_var_values
If a variable has been assigned to fill using fill_var, this allows you to modify the colours assigned to the fill of each of the variable groups, e.g. fill_var = grouping_variable, fill_var_values = c("blue", "red"). See
scale_fill_manualfor details. For the colour options available in base R, seecolour_options.- colour_var_values
If a variable has been assigned to colour using colour_var, this allows you to modify the colours assigned to the outline of each of the variable groups, e.g. colour_var = grouping_variable, colour_var_values = c("blue", "red"). See
scale_fill_manualfor details. For the colour options available in base R, seecolour_options.- palette
If a variable is assigned to fill_var or colour_var, this determines which viridis colour palette to use. Options include "plasma" or "C" (default), "magma" or "A", "inferno" or "B", "viridis" or "D", and "cividis" or "E". See this link for examples. You can override these colour palettes with fill_var_values or colour_var_values.
- palette_direction
Choose "d2l" for dark to light (default) or "l2d" for light to dark.
- palette_begin
Value between 0 and 1 that determines where along the full range of the chosen colour palette's spectrum to begin sampling colours. See
scale_fill_viridis_dfor details.- palette_end
Value between 0 and 1 that determines where along the full range of the chosen colour palette's spectrum to end sampling colours. See
scale_fill_viridis_dfor details.- alpha
This adjusts the transparency/opacity of the graphical components of the plot, ranging from 0 = 100% transparent to 1 = 100% opaque.
- greyscale
Set to TRUE if you want the plot converted to greyscale.
- line_size
Controls the thickness of the bar outlines.
- coord_flip
Flips the x and y axes. See
coord_flipfor details.- theme
Adjusts the theme using 1 of 6 predefined "complete" theme templates provided by ggplot2. Currently supported options are: "classic", "bw" (the elucidate default), "grey" (the ggplot2 default), "light", "dark", & "minimal". See
theme_bwfor more information.- text_size
This controls the size of all plot text. Default = 14.
- font
This controls the font of all plot text. Default = "sans" (Arial). Other options include "serif" (Times New Roman) and "mono" (Courier New).
- facet_var
Use if you want separate plots for each level of a grouping variable (i.e. a faceted plot), e.g. facet_var = "grouping_variable" or facet_var = grouping_variable. See
facet_wrapfor details.- facet_var_order
If a variable has been assigned for faceting using facet_var, this allows you to modify the order of the variable groups, e.g. facet_var = grouping_variable, facet_var_order = c("group_2", "group_1"). See
fct_relevelfor details.- facet_var_labs
If a variable has been assigned for faceting using facet_var, this allows you to modify the labels of the variable groups which will appear in the facet strips, e.g. facet_var = grouping_variable, facet_var_labs = c("group_1_new_label" = "group_1_old_label", "group_2_new_label" = "group_2_old_label"). See
fct_recodefor details.- facet_var_strip_position
If a variable has been assigned for faceting using facet_var, this allows you to modify the position of the facet strip labels. Sensible options include "top" (the default) or "bottom".
- facet_var_text_bold
If a variable has been assigned for faceting using facet_var, this allows you to use boldface (TRUE/default or FALSE) for the facet strip label text.
- legend_position
This allows you to modify the legend position. Options include "right" (the default), "left", "top", & "bottom".
- omit_legend
Set to TRUE if you want to remove/omit the legends.
- interactive
Determines whether a static ggplot object or an interactive html plotly object is returned. See
ggplotlyfor details.- aesthetic_options
If set to TRUE, opens a web browser to the tidyverse online aesthetic options vignette.
Value
A ggplot object or plotly object depending on whether static or interactive output was requested.
References
Wickham, H. (2016). ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. New York, N.Y.: Springer-Verlag.
See also
Examples
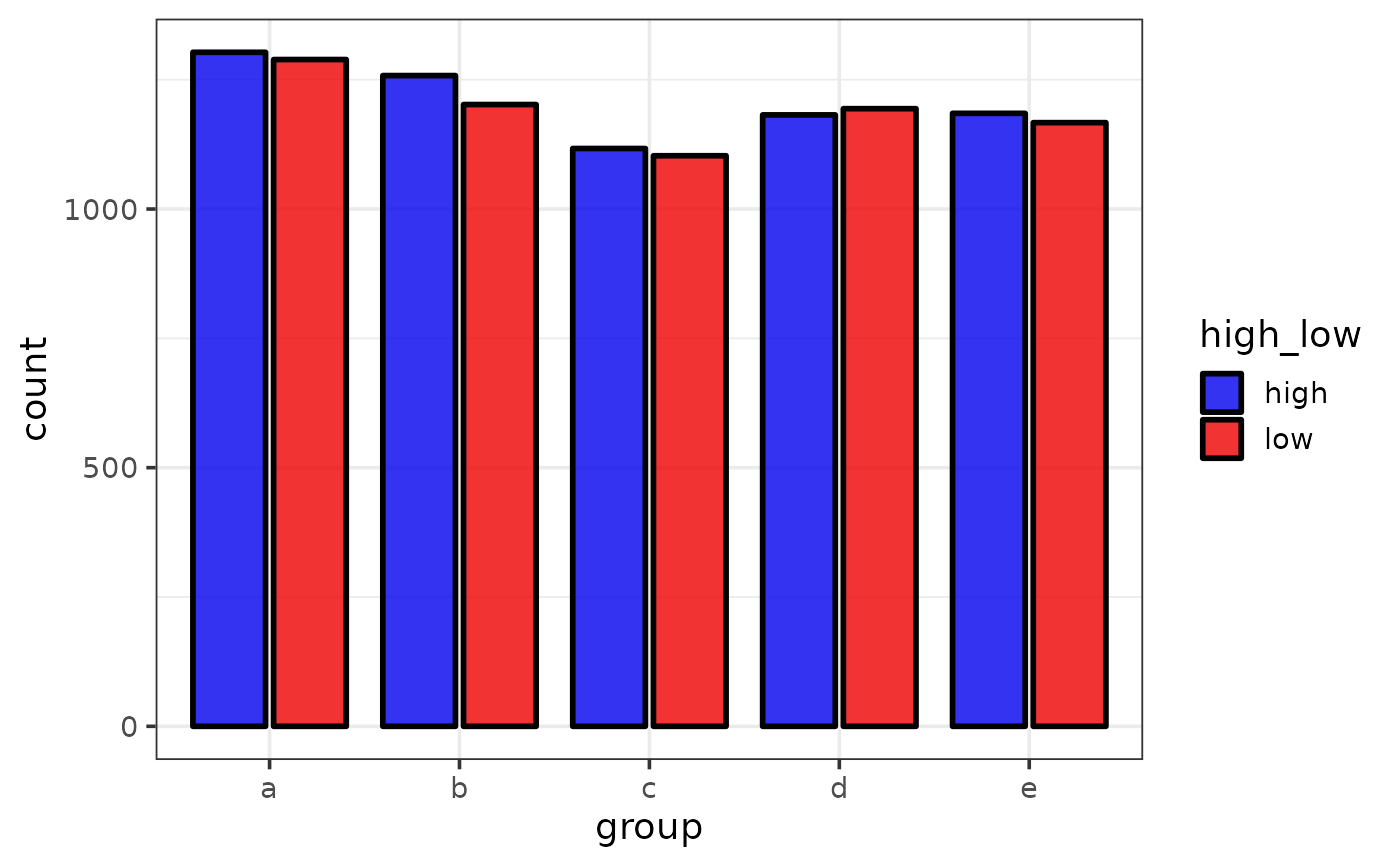
#plotting group counts
plot_bar(pdata,
x = g,
xlab = "group",
fill_var = high_low,
colour = "black",
fill_var_values = c("blue2", "red2"))
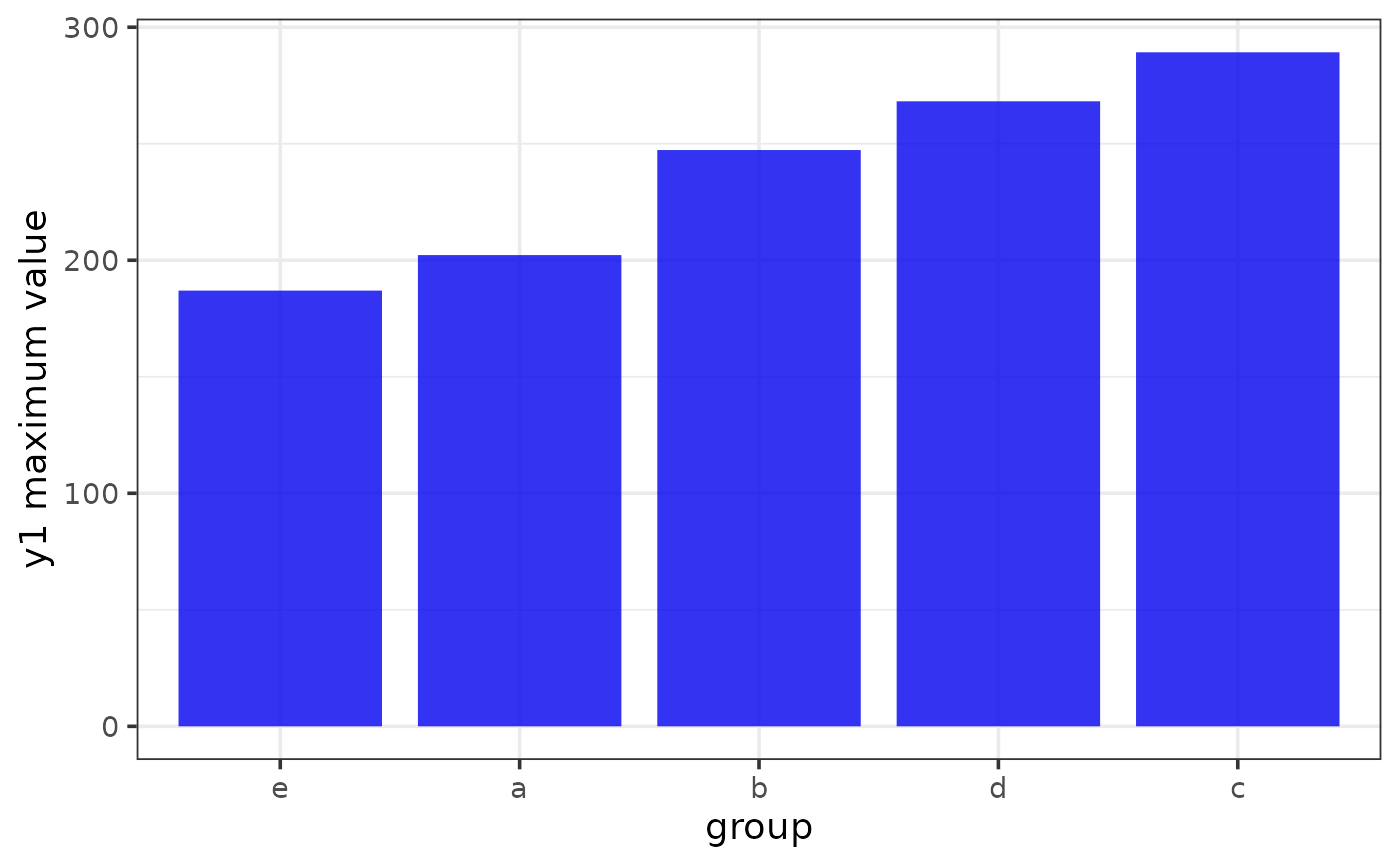
 #plotting specific values on the y-axis, e.g. a grouped summary statistic
library(dplyr)
#>
#> Attaching package: ‘dplyr’
#> The following objects are masked from ‘package:stats’:
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from ‘package:base’:
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
grouped_y1_max <- pdata %>%
group_by(g) %>%
summarise(y1_max = max(y1), .groups = "drop")
plot_bar(grouped_y1_max, x = g, y = y1_max,
xlab = "group", ylab = "y1 maximum value",
x_var_order_by_y = "i", #order levels of x by increasing y value
fill = "blue2")
#plotting specific values on the y-axis, e.g. a grouped summary statistic
library(dplyr)
#>
#> Attaching package: ‘dplyr’
#> The following objects are masked from ‘package:stats’:
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from ‘package:base’:
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
grouped_y1_max <- pdata %>%
group_by(g) %>%
summarise(y1_max = max(y1), .groups = "drop")
plot_bar(grouped_y1_max, x = g, y = y1_max,
xlab = "group", ylab = "y1 maximum value",
x_var_order_by_y = "i", #order levels of x by increasing y value
fill = "blue2")